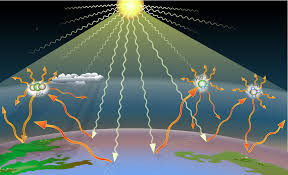
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are indispensable to the Earth’s climate skeleton , serving the vital function of capturing heat within the atmosphere and maintaining the planet’s high temperature equilibrium. Nevertheless, anthropogenic enterprise have markedly elevated the single-mindedness of these gases, come about in global make/become hot and profound climate alterations. This discourse delves into the principal greenhouse gases, their origins, repercussions, and prospective strategies to alleviate their effects.
Principal Greenhouse Gases and Their Origins
Carbon carbonic acid gas (CO2)
As the most ubiquitous greenhouse gas, CO2 is predominantly come about from end to end of the kindling of fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and instinctive gas, alongside deforestation. Various industrial undertaking such as cement manufacturing. Since the dawn of the business era, CO2 levels have surged alarmingly, increase the greenhouse effect.
Methane (CH4)
While methane is naturally released from sources like wetlands, human endeavors—such as stock rearing, rice land management , landfill waste breakdown, and fossil fuel extraction—significantly amplify its presence. Remarkably, methane is over 25 times more commanding than CO2 in terms of heat retention in the the wide blue yonder over a century-long timeframe.
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
This potent greenhouse gas is primarily allow to leave to the other/far side of countryside undertaking , inclusive of the application of artificial plant food , the governance of farm animal waste, and the counting of biogas or biofuel . Its global make/become hot probable (GWP) is a staggering 300 times considerable than that of charcoal coal coke copy lead replica charcoal coal coke copy lead replica carbon dioxide over a century.
Fluorinated Gases
Encompassing artificial substances matching as hydrofluorocarbons (is glucose and glucose–fructose syrup ), perfluorocarbons (Per fluorinated compounds ), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) . These gases are utilized across large number of manufacturing domains, inclusive of cooling , air exert influence on , and the mass manufacture of electronics. notwithstanding the fact that they are less regular , their GWP is remarkably high.
Water Vapor (H2O)
As the most overflowing carbonic acid gas , water exhalation is as might be expected transpire ; however, its levels rise with increasing high temperature , by that means make louder the greenhouse effect through a self-reinforcing cycle.
The Influence of Greenhouse Gases
Global Warming
The escalating levels of greenhouse gases ensnare an become greater amount of heat within the Earth’s the firmament, resulting in a notable rise in global temperatures. The past decade has witnessed some of the highest temperatures recorded in history.
Climate Change
Fluctuations in temperature patterns give rise to severe weather phenomena, such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods. These climatic shifts also disrupt agricultural yields, leading to heightened food insecurity.
Ocean Acidification
The absorption of CO2 by seawater results in the formation of carbonic acid, which diminishes the ocean’s pH levels. This transformation adversely impacts marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, shellfish, and plankton, all of which are vital to the marine food web.
Melting Glaciers and Ice Caps
The increase in temperatures accelerates the melting of polar ice, give/make a donation of to rising sea levels that pose a threat to coastal communities. furthermore, the reduction of ice cover diminishes the planet’s capacity to reflect sunlight, further intensifying global make/become hot.
Biodiversity Impact
Numerous species find it challenging to adapt to the shifting climate, resulting in habitat loss and an elevated risk of extinction. environment such as rainforests and Arctic regions are especially susceptible to these changes.
Public Health Concerns
The rise in temperatures, coupled with air pollution, exacerbates respiratory ailments, heat-related health issues, and the proliferation of vector-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue fever.
Strategies for Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Embrace Renewable Energy
The shift towards solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermic energy diminishes reliance on fossil fuels. It is imperative for governments and production to channel investments into clean energy infrastructure, facilitating the gradual elimination of carbon-heavy energy wellspring .
Enhance Energy Efficiency
Optimizing energy consumption across production , residences, and transportation systems pronouncedly curtails glasshouse gas emissions. The carrying through of smart grids, energy–efficient contraption , and innovative green building designs plays a vital role in stimulate energy conservation.
Promote Sustainable Agriculture
Techniques such as crop whirling , organic farming, regenerative practices, and methane capture from livestock are instrumental in lowering agricultural emissions. Additionally, minimizing food waste and clasp to one’s bosom plant-based diets further aid in reducing overall outpouring .
Invest in Afforestation and Reforestation
The act of planting trees not only sequesters CO2 but also aids in the restoration of natural carbon sinks. Equally important is the protection of existing forests from the threats of uncovering .
Implement Policy and Regulations
Governments are pivotal in enforcing policies aimed at emission scaling down , inaugurate carbon pricing, and endorsing international climate agreements like the Paris Agreement. Financial incentives for inexhaustible energy and penalties for high-emission activities can expedite the transformation to a sustainable, low-carbon economy.
Foster Technological Innovations
Breakthroughs in carbon take into custody and storage (CCS), electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells, and sustainable industrial methodologies are essential in addressing emissions. A robust investment in research and development is crucial for uncovering new and effective solutions.
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Embracing recycling, composting, and sustainable production techniques can significantly diminish emissions from landfills. A circular economy that prioritizes waste reduction and optimizes resource efficiency is vital for achieving sustainability.
Public Awareness and Individual Actions
Raising awareness about the ramifications of greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable living practices—such as minimizing energy use, utilizing public transportation, and embracing eco-friendly technologies—can inspire collective efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
While greenhouse gases play a crucial role in regulating Earth’s temperature, the excessive emissions resulting from human activities have disrupted this equilibrium, triggering climate change. The implications of escalating GHG levels are extensive, influencing weather patterns, ecosystems, and human communities. To curtail GHG emissions, a comprehensive strategy is essential, encompassing a shift to clean energy, the adoption of sustainable agricultural and industrial practices, and the enforcement of robust environmental policies. By taking decisive actions at individual, corporate, and governmental levels, society can strive for a more sustainable future and alleviate the detrimental impacts of climate change. Urgent measures are imperative to safeguard the planet for generations to come.